CogPaths provide a good way to get a reference to any Cog anywhere within a game session. It points directly to the object as identified in the editor (or through a written file path) instead of wasting valuable computation time searching for it in code. As such, it is usually best to instantiate any CogPath variables before run-time
The CogPath Property
To use a CogPath cogPath property in a component, a CogPath variable with the [Property] attribute is necessary:
[Property] var ObjectCogPath : CogPath = CogPath();
When viewed in the Properties window, a CogPath property will appear:
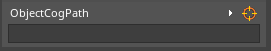
Selecting the object the CogPath refers to may be done in one of three ways: from the Level Editor window, the Objects window, or by typing it in directly
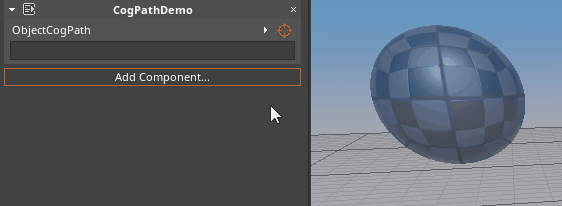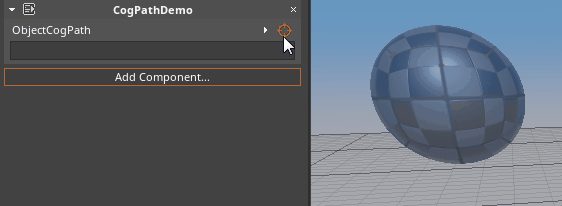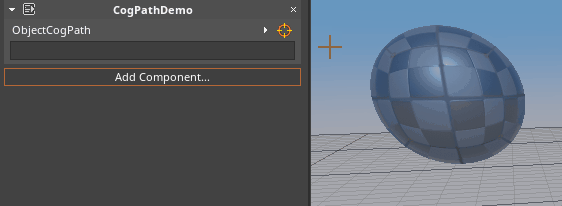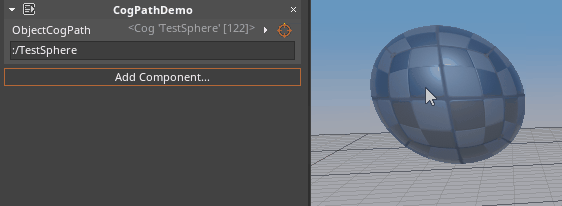
- To select from the Level Editor:
- Hold Left-Click over the Orange reticle icon and Drag over to the object in the Level Editor window:
- To select from the Objects window:
- Hold Left-Click over the Orange reticle icon and Drag over the object name in the Objects window:
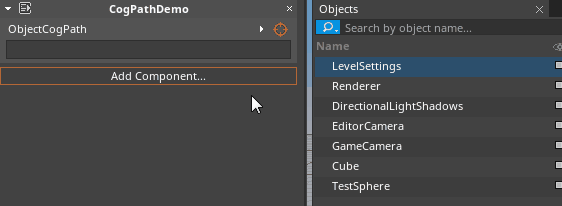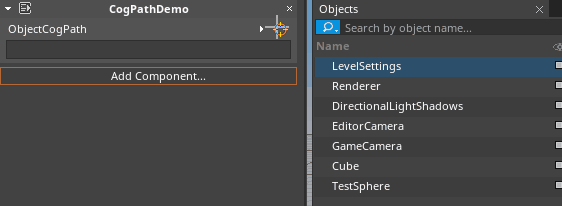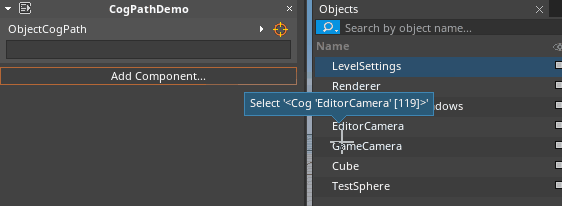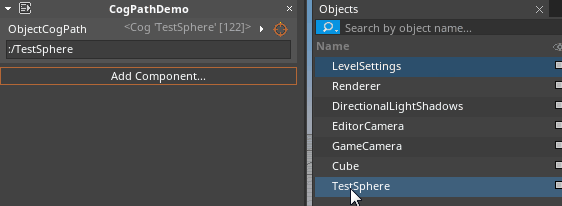
- To select by typing the name in directly:
- The syntax is very similar to a file system hierarchy. The space that the object is in acts as the "Drive Name" (
this.Space:/), which allows a CogPath to reference a Cog in a different Space than the one the object with the component exists in. If the object is in the space that the component is in, you do not need to type in the space (i.e. just:/):
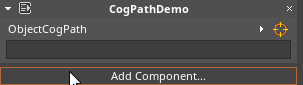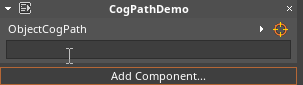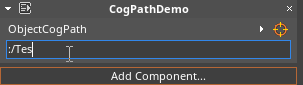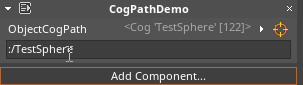
To access the Cog that the CogPath points to, simply use the dot operator after the name of the CogPath variable:
var myObject = this.ObjectCogPath.Cog;
In-Editor Properties of CogPath
Once an object has been selected, a number of different options become available. These may be accessed in the Properties window by clicking on the arrow icon next to the orange reticle, like so:
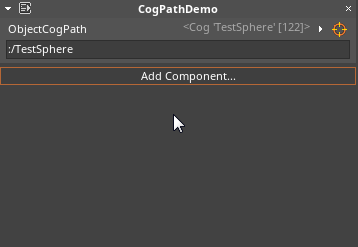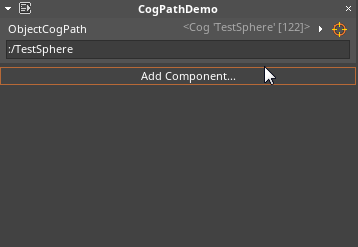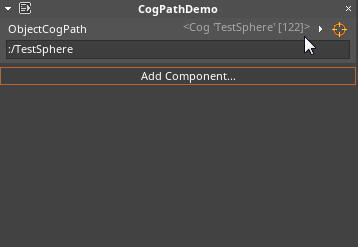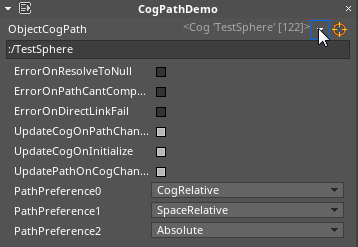
| Editor Property | Description |
|---|---|
| DirectCog drop-down menu | If the current cog is null, and it is accessed through CogPath.Cog, it will try to resolve the path. DirectCog never tries to resolve the path. It's a pointer to the object |
| ErrorOnResolveToNull checkBox | Is an exception thrown if a Cog is accessed when it's invalid or not found? |
| ErrorOnPathCantCompute checkBox | Throw an exception/notification if the path to an object cannot be computed? |
| ErrorOnDirectLinkFail checkBox | Throw an exception/notification if a direct link to the object cannot be resolved? |
| UpdateCogOnPathChange checkBox | When cog path is set, should object be resolved? (this also detects parse errors) |
| UpdateCogOnInitialize checkBox | Whether the cog path attempts to resolve an object when the object is fully initialized |
| UpdatePathOnCogChange checkBox | When the cog is set, should the path to the object be recomputed? |
CogRelative (Path Preference) |
First attempt to represent the path as a relative path. This is only valid if the objects are on the same hierarchy (such as .. for parent, ../OtherObject for a sibling, or Child1/Child2 for children) |
SpaceRelative (Path Preference) |
Assumes the objects are not on the same hierarchy, but exist within the same space. This means all paths begin with :/, which means look within the same space. |
Absolute (Path Preference) |
Always require a named space (such as Hud or Main) and then a full path to the object such as Hud:/HealthText. Note that Absolute can only be used in the editor with the orange reticle target picker if the space is given a name. |