Roughness quite simply defines how rough--or conversely, how smooth--a particular material is. The greater the roughness of a surface, the greater the diffusion of light that hit that surface. Roughness can be defined either by value, which is uniformly applied across the surface of a Material, or by texture map, which defines the roughness value for each discrete part of the Material.
Roughness as defined in the deferred renderer follow microfacet theory, in which surface irregularities on the Material cause reflected light to "blur". The higher the Roughness value, the greater the blurring effect will be. For a quick look at how increasing roughness corresponds to increased blur, the following screenshot shows spheres with constant albedo and metallic , but an increasing value of roughness from 0 to 1:
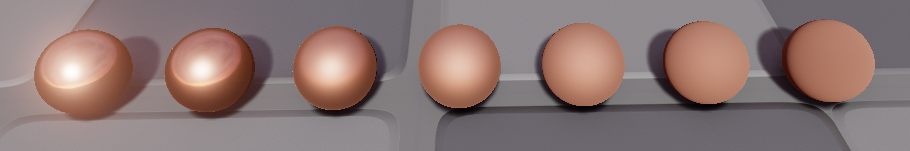
Especially through the first five or six spheres, as the roughness goes up, the reflection gets progressively more pronounced until individual objects reflected from the skybox are no longer visible.
The Roughness Fragment
Roughness may be set using a value or a texture map. If a value is used it is applied uniformly across the surface of the Material. If a texture map is used, the Roughness value may be set to different values ranging from 0 to 1 across the surface of the Material.
Roughness Value
When the RoughnessValue fragment is applied, the roughness value specified will be applied uniformly across the surface of the Material. To add a RoughnessValue fragment, click on the the Add NadaFragment button in the Material Properties window and select RoughnessValue, as seen below:
Roughness Map
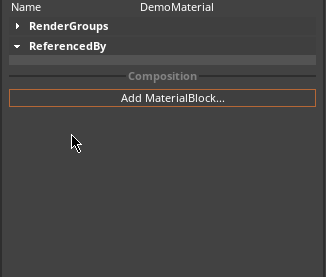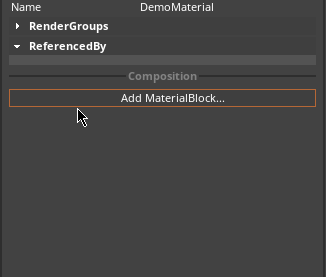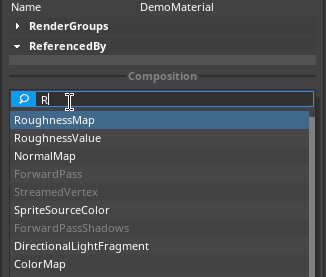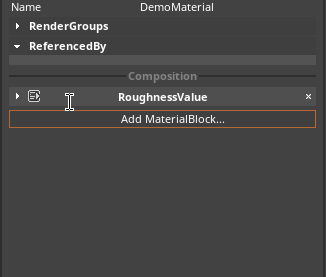
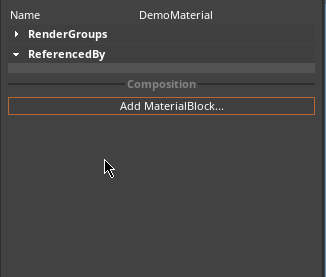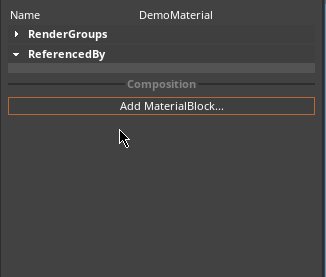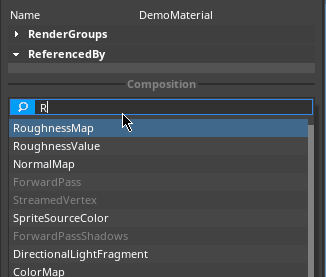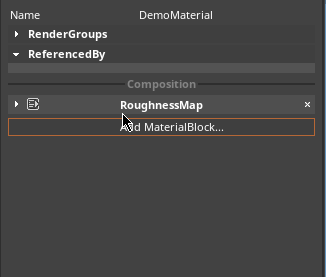
When the RoughnessMap fragment is applied, different roughness values are applied to discrete sections of the Material, as dictated by the texture map. To add a RoughnessMap MaterialBlock, click on the Add MaterialBlock button in the Material Properties window and select RoughnessMap, as seen below:
RoughnessMaps may be broken down into two broad categories: tileable roughness maps, which can be used on any model, and model-specific roughness maps, which are intended to be used with a specific model or set of models.