CapsuleCollider defines a capsule shape for collision. The base size of the capsule is determined by the Radius and Height properties. Scale is applied afterwards to determine the final capsule's size.
Capsules are often used as a combination of cylinders and ellipsoids for collision, primarily for long thin shapes. An ellipsoid tends to be undesired when stretched on one axis due its curved sides. A cylinder fixes this but loses the curved caps of the ellipsoid. A capsule combines these by having a cylinder that can be scaled in one axis while containing smooth edge caps.
Capsules are also commonly used for a player. The player's height can be scaled without affecting its width. Additionally, the curved caps help to avoid edge catching issues.
(NOTE) Recommended Reading: The Collider page should be read before this page.
Radius
Radius defines the radius of the capsule in local space.
Height
Height defines the local space height of the cylinder. The height is defined as the distance from the center of the bottom sphere to the center of the top sphere.
Direction
Direction enum is used to configure which local-space axis the height of the capsule runs along. This allows aligning a capsule with an asset that was configured about a different axis.
Scaling Mode and Non-Uniform Scale
Like most other Collider types, CapsuleCollider will maintain a perfect capsule shape when non-uniform scale is present. That is to say that the spherical caps on the end of the capsule will always be perfect spheres, never ellipsoids. This creates a dilemma when non-uniform scale is applied to the height axis. There's two different behaviors that a user could expect that is controlled via ScalingMode enum:
ScalingMode.PreserveScale
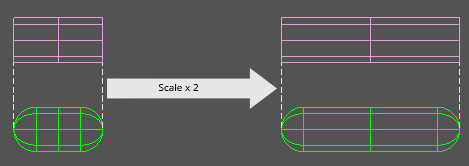
PreserveScale applies scale to the full height of the capsule (including the end caps). The easiest way to understand this mode is by comparing it to a cylinder with the same total height as the capsule, both of which are pictured on the left. After scaling both objects their total heights should be the same as pictured on the right.
To fully understand what this is doing requires a numerical example. In the above picture, the capsule has a height of 1 and a radius of 0.5. The capsule's total height is 2 (height + 2 * radius). After scaling, the total height should now be 4, however no scale was applied in the y-axis so the radius must stay at 0.5. This means that the capsule's world height must be 3 after scaling (height = 4 - 2 * radius).
ScalingMode.PreserveHeight
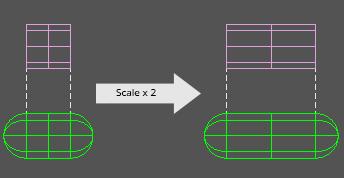
PreserveHeight applies scale just to the capsule's height (not including the end caps). The easiest way to understand this is to compare to a cylinder with the same height as the capsule (pictured on the left). After scaling, the internal cylinder of the capsule matches the scaled cylinder (pictured on the right).
This mode does not preserve the total scale of the capsule though. The original capsule had a total height of 2. Since no scale was applied in the y-axis, the radius has to stay at 0.5. Now the scaled capsule has a height of 2 with a radius of 0.5 which produces a total height of 3.
This mode is often desired when a model is attached to a cog that should match the inner cylinder. Additionally, this can be useful when game-logic cares about the positioning of the cap centers as opposed to the tips of the capsule.